Parts Of Lathe Machine
- Lathe Bed
- Headstock
- Tailstock
Major parts that are incorporated in lathe machine are:
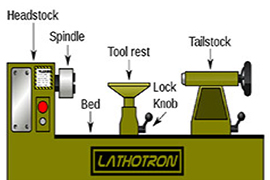
A lathe may or may not have legs which sits on the floor and elevates the lathe bed to a working height. Some lathes are small and sit on a workbench or table, and do not have a stand.
At one end of the bed (almost always the left, as the operator faces the lathe) is a headstock. The headstock contains high-precision spinning bearings. Rotating within the bearings is a horizontal axle, with an axis parallel to the bed, called the spindle. Spindles are often hollow, and have exterior threads and/or an interior morse taper on the “inboard” by which work-holding accessories may be mounted to the spindle.
The spindle is driven, either by foot power from a treadle and flywheel or by a belt or gear drive to a power source. In most modern lathes this power source is an integral electric motor, often either in the headstock, to the left of the headstock, or beneath the headstock, concealed in the stand.
The counterpoint to the headstock is the Tailstock, sometimes referred to as the loose head, as it can be positioned at any convenient point on the bed, by undoing a locking nut, sliding it to the required area, and then re-locking it. The tail-stock contains a barrel which does not rotate, but can slide in and out parallel to the axis of the bed, and directly in line with the headstock spindle.
Metalworking lathes have a carriage (comprising a saddle and apron) topped with a cross-slide, which is a flat piece that sits crosswise on the bed, and can be cranked at right angles to the bed. Sitting atop the cross slide is usually another slide called a compound rest, which provides 2 additional axes of motion, rotary and linear.
Woodturning and metal spinning lathes do not have cross-slides, but rather have banjos, which are flat pieces that sit crosswise on the bed. The position of a banjo can be adjusted by hand; no gearing is involved. Ascending vertically from the banjo is a tool-post, at the top of which is a horizontal tool-rest.
In the craft of woodturning, a banjo is a common term for a fixture on the wood lathe, mounted on the lathe’s bed, for holding the toolrest. It allows for adjustment of the toolrest in various positions, by the lathe operator, making it possible to hold the turning tool in the most convenient position for removing material from the spinning wood.
In woodturning, hand tools are braced against the tool rest and levered into the workpiece. In metal spinning, the further pin ascends vertically from the tool rest, and serves as a fulcrum against which tools may be levered into the work-piece.






